Covered Bond Swaps

Richard Kemmish
30 years: Capital markets & covered bonds
One of the problems many covered bonds have to address is the mismatch between the interest rate on the assets and the interest rate on the bonds. Richard discusses how swaps are used to address this mismatch by explaining how swaps work, explaining how they are documented and providing some examples.
One of the problems many covered bonds have to address is the mismatch between the interest rate on the assets and the interest rate on the bonds. Richard discusses how swaps are used to address this mismatch by explaining how swaps work, explaining how they are documented and providing some examples.
Subscribe to watch
Access this and all of the content on our platform by signing up for a 7-day free trial.

Covered Bond Swaps
8 mins 33 secs
Swaps are utilised to address the main issue of the mismatch between the interest rate on bonds and the interest rate on assets by finding a willing counterparty to trade with.
Key learning objectives:
Identify the basic problems
Explain how Swaps and 2-Swaps work
Describe how to mitigate credit risks
Outline the ways in which covered bonds are documented
Subscribe to watch
Access this and all of the content on our platform by signing up for a 7-day free trial.
What are the basic problems?
- The majority of covered bonds are fixed rates
- Most mortgages are either floating-rate or are fixed-rate for a short time period only
- For some countries like the UK and Canada, they have a mismatch between the currency on the mortgages and the euro in which most of their covered bonds are denominated
- Most covered bond pools are backed by 10,000s or 100,000s of individual mortgages
- Most banks offer various interest-rate options over time
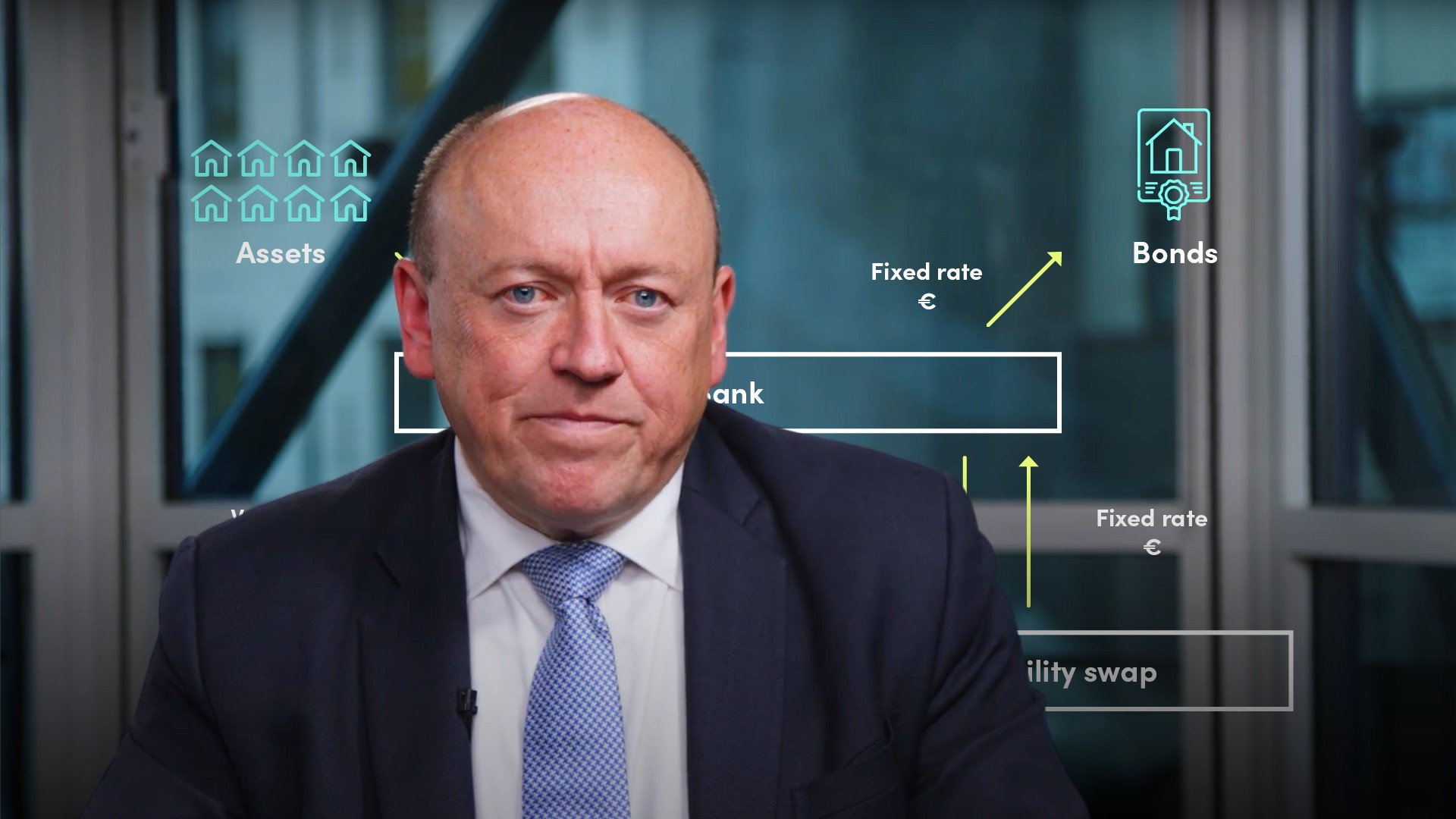
How do swaps work?
The interest payments are taken on the assets (the floating rates coming off all the mortgages) and a counterparty is found who is prepared to swap them for the fixed-rate interest payments on the covered bonds.
The first swap takes all of the rates on all of the assets in the mortgages covered pool that month and switches these cashflows into one, simple rate. The second swap is more standard. Here the swap counterparty pays the issuer the coupon on the bond and in return receives LIBOR plus a spread matching one leg of the asset swap.
How are credit risks mitigated?
- You could enter into swaps with counterparties that aren’t going to default. However, these counterparties don’t exist.
- The swap counterparty has to post collateral to the issuer to protect it from losing the value of the swap. If the swap counterparty fails, this collateral can be used to compensate the cover pool and allow it to replace the swap counterparty.
How are covered bond swaps documented?
One of the standard terms in swap documentation, and a requirement of clearing houses, is that the collateral posting – the initial margin and the variation margin - goes both ways. Either counterparties of a swap have to provide it. Another unusual feature of covered bond swap documentation is that it doesn’t allow automatic termination on insolvency.
Also, the EMIR Regulations requiring clearing have a specific carve-out for covered bonds, so they don’t attract additional capital charges and can continue to provide protection for the holders of the covered bonds.
Subscribe to watch
Access this and all of the content on our platform by signing up for a 7-day free trial.

Richard Kemmish
There are no available videos from "Richard Kemmish"






















