Introduction to Derivatives

Gontran de Quillacq
25 years: Derivatives trading & ETFs
A derivative is a financial product, whose price is derived from the price of another product. In this video Gontran briefs us about the history of derivatives and exchanges. He further explains the types of derivatives along with the usages and also highlights it's advantages and disadvantages.
A derivative is a financial product, whose price is derived from the price of another product. In this video Gontran briefs us about the history of derivatives and exchanges. He further explains the types of derivatives along with the usages and also highlights it's advantages and disadvantages.
Subscribe to watch
Access this and all of the content on our platform by signing up for a 7-day free trial.

Introduction to Derivatives
18 mins 49 secs
Key learning objectives:
Understand the history of derivatives and exchanges.
Define Derivatives and outline the types of derivatives
Define counterparty risk
Outline the three key things to learn about derivatives exchange
Understand why we should use derivatives
Overview:
It is difficult to make money in trading, but it is very easy to lose some. When it comes to derivatives, you're up against experts who are better educated, better trained, better controlled, and have far more resources than you to deal with adversity. Hence, it is advised to be careful while trading in derivatives and not overextend ourselves financially with products you may not understand well.
Subscribe to watch
Access this and all of the content on our platform by signing up for a 7-day free trial.
What is the history of derivatives and exchanges?
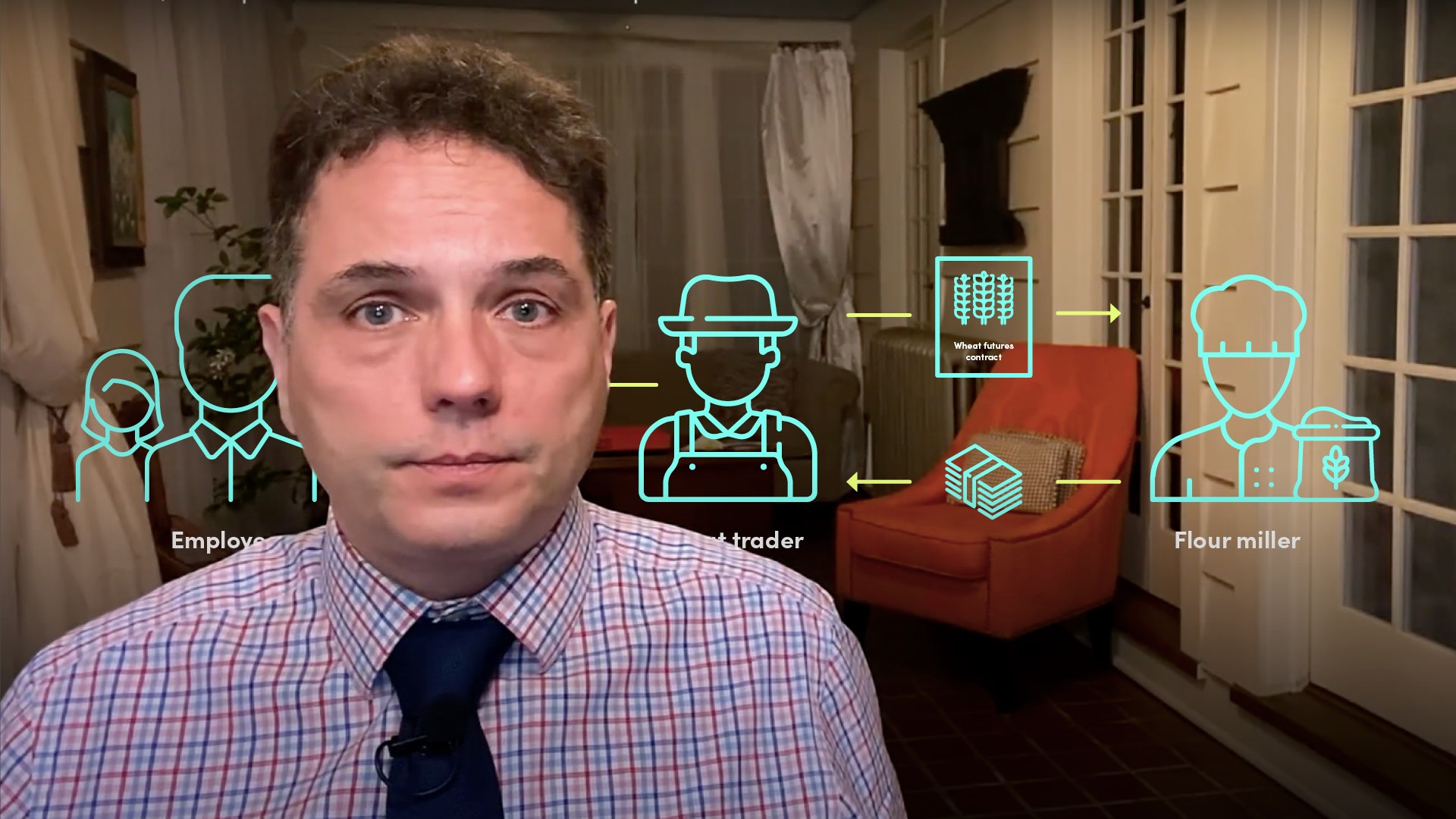
Chicago had always been a centre of commodity trade, and many farmers would bring their crop to the central market. Wheat farmers would meet with flour millers or bread bakers, hands would be shaken, and carts would transport the harvest to the factories. Those who unfortunately arrived last, often found no buyers for their harvest. This often meant disaster for the farmers, as many would literally abandon their crop in the street.
A solution needed to be found, and the CBOT was formed in 1848 with corn futures. The great innovation of a futures contract is that buyers and sellers could agree to trade (quantity, quality, price…), but the settlement would occur at a later date. With the success of the concept with corn, more commodities were introduced – wheat, soybean, cocoa, sugar... New exchanges appeared (cotton, with the New York Cotton Exchange created in 1870) and the Chicago mercantile exchange ( in1898, with beef and pork).
What are Derivatives and its types?
A financial product, whose price derives from the price of another product. It typically specifies a payout and a time. Derivatives are usually defined in two main categories:
- Over-the-counter - These are agreements between two individuals, which trade away from any regulated or listed market
- Listed - These are derivatives traded on an exchange. The exchange specifies rules, as well as the contract definition
What is Counterparty risk?
The risk that your counterparty doesn't pay you, usually because it defaults before paying you.
What are the three key features about Derivatives Exchanges?
- It sets the rules for operations, in particular, the minimum payment at the onset of the trade (the initial margin).
- Specify how money will be exchanged during the lifetime of the product (variation margin).
- Not everybody can trade on an exchange. They set financial strength requirements for its members with the help of 'clearers'. A clearer is a very well capitalised financial company, which guarantees the financial payments of a given market participant (the trader) who clears through it.
What are the main types of Derivatives?
- Futures
- Options
- Forwards
- Swaps
- ETFs
What are the legal forms of Derivatives?
- OTC forward contract - It has counterparty risk, while a listed futures contract which is virtually the same payout has no counterparty risk
- ETF - These are securities traded on a stock exchange. An ETF may contain counterparty risk on the issuer, even if the issuer is listed on the exchange
- A debt instrument - A convertible bond is a debt instrument. Most structured products sold by banks to investors through RIAs and wealth management are actually debt instruments
Why should we use derivatives?
- You can eliminate an existing exposure: you are therefore hedging a risk
- You can eliminate a risk or you can add exposure through a derivative based on your analysis, and speculate that the risk will go in your favour
What are the benefits of using derivatives?
- Trade risk
- There is no uptick rule for derivatives
- Derivatives are easy to short
- No borrowing fees for contracts
What are the downsides of using derivatives?
- You can take the wrong risk at the wrong time
- Since you can trade on margin, you may over-leverage yourself and over-extend your financial capacity
- You may still have counterparty risk or regulatory risk
Subscribe to watch
Access this and all of the content on our platform by signing up for a 7-day free trial.

Gontran de Quillacq
There are no available Videos from "Gontran de Quillacq"



























