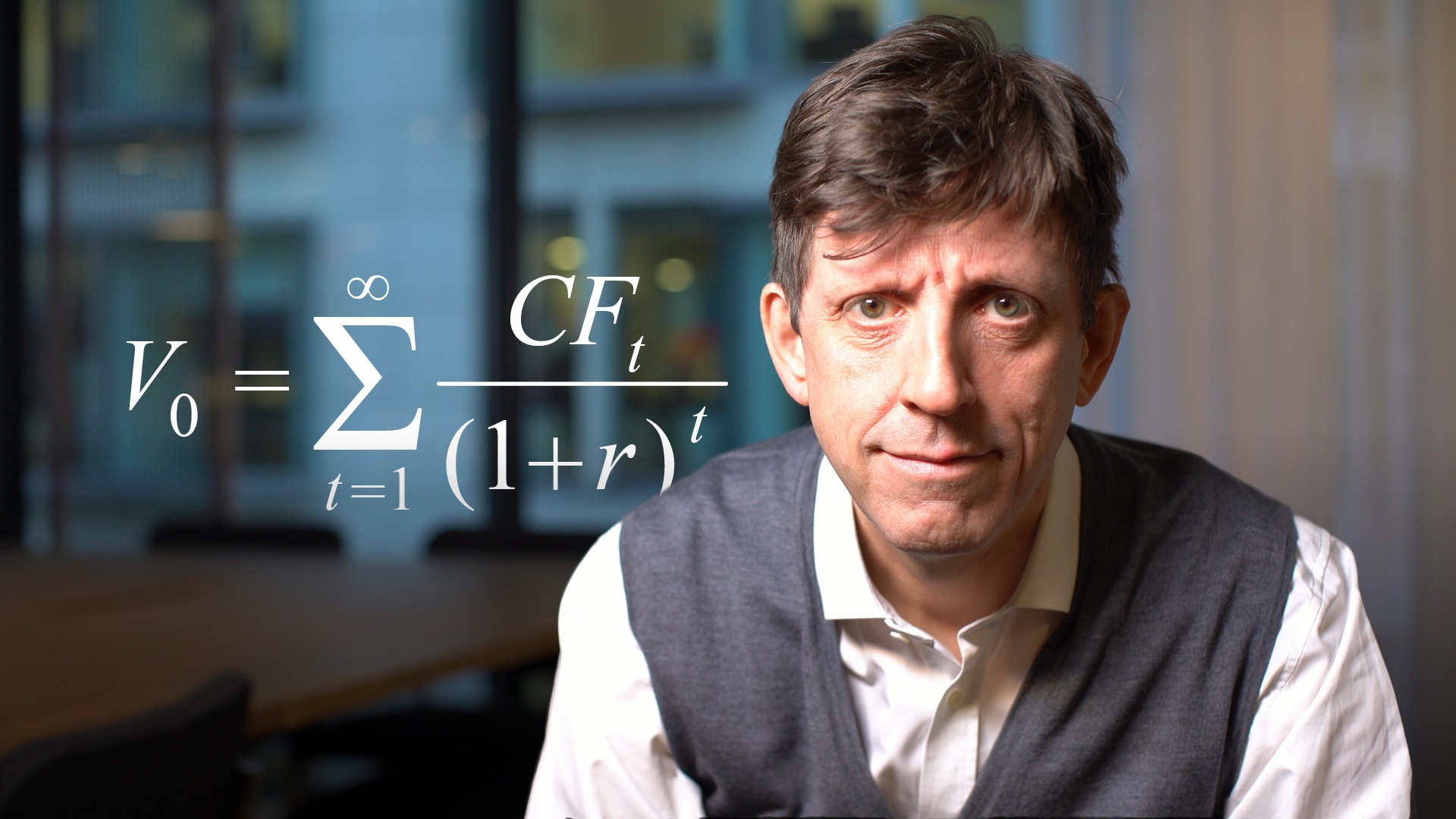Perpetual Bond
Perpetual bonds (perps) are hybrid debt instruments in that they share elements of debt and equity. As their name suggests, perps have no maturity date. The instruments remain in issue in perpetuity if issuers fail to exercise options to call the bonds. In the case of non-calls, holders will never receive their principal back from the issuer. Some perps have so-called step-up features where the coupon increases in the event they are not called. If issuers do opt to call the bonds, the call price could be below the price at which an investor bought the securities. An investor’s only recourse to get principal back is to sell the perp to another investor. Perps carry high interest rates, but issuers have the right not to pay coupons. Also, perps are non-cumulative instruments, meaning if an issuer opts not to pay a certain coupon, it has no obligation to make good on that missed payment at a later date. In the event of issuer insolvency, perp holders will be near the back of the repayment queue i.e. in front of shareholders but behind secured and senior unsecured creditors.